
Fixing slow home network speeds is a common frustration for many homeowners. A sluggish internet connection can disrupt daily activities, from streaming videos to online gaming and video calls. This comprehensive guide will delve into the various causes of slow home network speeds and provide actionable solutions to optimize your home network’s performance. We’ll cover everything from identifying the root cause to troubleshooting the hardware and configuring network settings, and even some advanced techniques to fine-tune your network. Get ready to transform your frustratingly slow home network into a high-speed marvel!
Identifying the Root Cause of Slow Speeds
Understanding the Basics of Home Network Speed
Network speeds are fundamentally affected by a multitude of factors. From the router’s capabilities to interference from other devices and even the quality of the cables used in your home, everything plays a vital role in determining your internet speed. When you’re dealing with a slow home network speed, it’s crucial to pinpoint the source of the problem. This section explores some of the most common causes. Sometimes, the problem lies in simple solutions, like ensuring your router is positioned optimally.
Common Causes of Slow Home Network Speeds
- Faulty or outdated network hardware; Outdated or malfunctioning equipment, like your router or modem, can lead to significant slowdowns. It might be as simple as a failing network card or an outdated router that isn’t capable of handling today’s high-bandwidth activities.
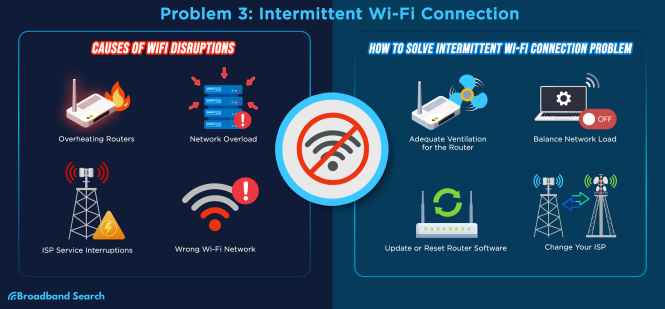
- Network congestion
The network could be overloaded with too many devices concurrently using the internet. Consider how many people in your home use Wi-Fi or cable internet simultaneously. A simple solution is to turn off devices that you’re not using.
- Interference from other electronic devices
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) can lead to fluctuations in your home network speed, as can issues with your home’s electrical wiring.
- Incorrect or poor network settings
An incorrect network configuration can affect signal strength and speed. Ensure your network settings are optimized for your specific needs.
- Outdated or improperly configured software
Check for outdated network drivers and ensure all devices have the latest updates installed, to take advantage of any possible optimizations. This could make a big difference!
Troubleshooting Network Hardware
Evaluating Your Router
Your router is the central hub of your home network. It’s essential to verify that your router is compatible with your current internet plan, and that it’s capable of handling all the devices trying to connect. Check for firmware updates and consider upgrading to a newer router if necessary. A faster, more advanced router will be able to handle high bandwidth demands. Consider factors such as speed, range, and signal strength when you decide what router to use, ensuring compatibility between your devices and the infrastructure.
Examining Your Modem
Your modem is responsible for connecting your home network to the internet. It’s essential to ensure that your modem is in good working order. Similar to your router, ensure your modem is compatible with your current internet plan. Examine the modem and any cables or wires for any physical damage that may be affecting your internet speed.
Cable Quality
A crucial but often overlooked element is the quality of your cables. Faulty ethernet cables can cause signal degradation, leading to slower speeds. Ensure the cables are not damaged or frayed. Using high-quality, properly shielded cables can make a difference. If the cables are damaged, get them replaced or use a different connection type if there are any available. Testing cables for quality and correct connection can fix the issue and improve your internet speed.
Optimizing Network Settings
Configuring Your Wi-Fi
Adjusting your Wi-Fi settings can significantly impact your network speed. Ensure your Wi-Fi channels aren’t overlapping with those of nearby networks and are set to the best available channel and bandwidth.
Prioritizing Connections
Prioritizing important devices or applications can significantly improve your network speed and stability. Certain devices should be prioritized in the Wi-Fi network, based on their importance. For example, video streaming devices should receive priority, while other devices, such as those performing routine tasks, can be set to lower priorities.
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
Network Speed Tests and Metrics
Conduct thorough network speed tests to identify potential bottlenecks. Tools such as Ookla’s Speedtest are useful for establishing a baseline of your speed, and pinpointing slowdowns. A speed test is an essential first step for troubleshooting a slow internet connection.
Identifying and Addressing Interference
Identify potential sources of interference, like microwaves or cordless phones, which can interfere with your Wi-Fi signal. Avoid placing your router near these devices. Experiment with different locations for the router, such as moving it from a corner to a more central location. Experiment with these different locations to see what works best for you.
Advanced Router Configuration
Adjusting advanced router settings can often improve performance; however, improper adjustments can lead to further problems. Refer to your router’s manual for advanced configuration options, which may require specialized knowledge.
Conclusion
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[ ]
[]
In conclusion, fixing slow home network speeds often involves a combination of troubleshooting steps. Understanding the root cause, whether it’s a faulty router, congested network, or outdated hardware, is crucial. By implementing the strategies discussed above, you can significantly improve your home network’s performance and enjoy a smoother, faster online experience. Don’t hesitate to contact your internet service provider for further assistance if necessary. Learn how to optimize your network for peak performance today!